The yen is the official currency of Japan.
On the global forex market, the Japanese yen is the third most traded currency by value.
Most traded currencies by value (April 2016):
| Rank | Currency | % of daily trades (bought or sold) in April 2016 |
| 1 | United States dollar | 87.6% |
| 2 | Euro | 31.4% |
| 3 | Japanese yen | 21.6% |
| 4 | Pound sterling | 12.8% |
| 5 | Australian dollar | 6.9% |
The yen is a commonly used reserve currency, but it is not as popular as the giants USD, EUR and GBP.
The basics
Name: Japanese  yen
yen
Sign: ¥
Code: JPY
Alternative abbreviation: JP¥
Japanese symbol: 円 (modern), 圓 (traditional)
1 Japanese sen consists of 100 sen.
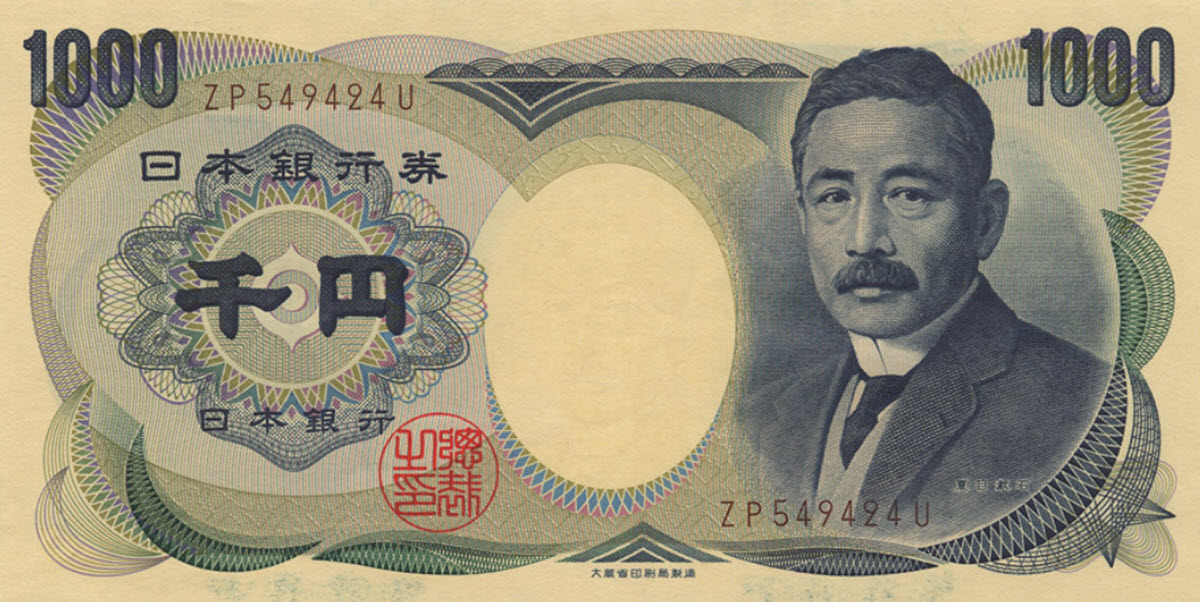
The most frequently used banknotes: ¥1000 / ¥5000 / ¥10,000
Coins: ¥1 / ¥5 / ¥10 / ¥50 / ¥100 / ¥500
Central bank: Bank of Japan
Printer: National Printing Bureau
Minter: Japanese Mint
History
In 1868, practical imperial rule was restored in Japan under Emperor Meiji. This is known as the Meiji Restoration. The Meiji government set out to modernize Japan’s economy, and as a part of this, they introduced a uniform currency throughout the empire and modeled it after the European decimal system. Prior to the Meiji Restoration, each of Japan’s many feudal fiefs issued their own scrip (hansatsu) for use within their territory, and this supplemented the coinage issued by the shogunate. Most hansatsu carried a face value in silver, but gold, copper and edible commodities such as rice were also common backers. Hansatsu was issued in an array of denominations and each feif made up their own system.
The New Currency Act of 1871 abolished the hansatsu and the shogunate coinage, and established the yen as currency for the whole empire. In the act, the yen was defined as 1.5 grams of gold or 24.26 grams of silver.
In 1882, the Bank of Japan was founded and given a monopoly on controlling the money supply in Japan.
The yen has been allowed to float since the end of the Bretton Woods system in 1971, but the Japanese government has maintained a policy of currency intervention since 1973, which is why the currency is considered a “dirty float”.
The Japanese government tries to ensure a low yen to aid the export market, and since the 1990s, the Bank of Japan has also kept the interest rates very low to spur economic growth. These low interest rates, and the high liquidity of the yen, has led to substatial carry trade, where investors borrow money in Japan and invest it abroad.
Coins
- The first yen coins were introduced in 1870. There were six silver coins and four gold coins. The silvers were 5 sen, 10 sen, 20 sen, 50 sen, and 1 yen. The gold coins were 2 yen, 5 yen, 10 yen, and 20 yen. The following year, a gold 1 yen was introduced as well.
- When a yen coin is minted, the year of the current emperor’s reign is put on the reverse side of the coin. Example: A yen coin minted in 2009 will me marked Heisei 21. This means the 21st year of Emperor Akihito’s reign.
- The value (expressed in kanji) is on the obverse side of the coin.
- Since 1946, 日本国 has been on the reverse side of the yen coins, except for the current 5 yen coin where 日本国 is on the reserve side. 日本国 means Nippon-koku, i.e. State of Japan. Coins minted 1945 or earlier will instead display 大日本, which means Dai Nippon (Great Japan).
- The 500 yen coin is one of the world’s highest-valued coins that’s in regular use. (As opposed to high valued commemorative coins and similar that are chiefly kept as collector items.) Data from February 2019 show that 500 yen equals 4 euro. Because of its high value, the 500 yen coin is a favorite among coin counterfeiters.

Banknotes
The first yen banknotes were issued in 1872, two years after the first yen coins. The smallest yen banknote ever issued is the 10 yen banknote.
The most recent yen banknote series, the series E, was introduced in 2004. It consists of just three notes: 1000 yen, 5000 yen and 10,000 yen.
Etymology
The name Yen is derived from the Japanese word for round, and is a cognate with the neighbouring monies Norther Korean won, South Korean won, and Chinese yuan (the basic unit of the currency renminbi).
Yen is the standard spelling and pronunciacion in English, even though it is pronounced en in Japanese.
This article was last updated on: March 13, 2019
